Explanation (which might be wrong, since I’m writing this after banging my head against a wall. Please do correct me if I’m wrong):
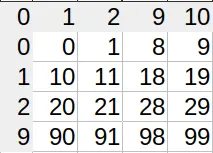
In regular numbering systems (i.e., decimal), we exhaust all 10 digits (0–9) before we reach two-digit numbers. The first number to require 3 digits is 10². The first to use 4 is 10³, and so on.
In music intervals, there is no “0”. The interval c’–c’, for instance, is called a prime (1). This has the funny consequence that moving by a fifth and then by a fourth doesn’t land you on the ninth, but the octave (8). Moving by an octave and then another octave gets you to the 15th, not the 16th.
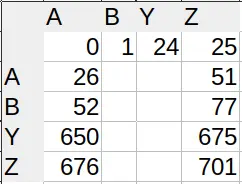
In Excel, shit hits the fan when you need to convert column names (A, B, C…) to numbers (0, 1, 2…). Since we use 26 characters as our ‘digits’, we’re in the hexavigesimal system. Knowing what I told you in the first paragraph, you’d expect the first double-digit column (AA) to be 26. And you’re right.
However, when do we need 3 digits? Which column is column AAA? A sane person would say it’s 26², so 676. Ha! No. Column number 676 is actually ZA. What gives? Well, we only ditch the zero for single digit numbers. All subsequent columns actually use 27 different characters, the ‘empty character’ being one of them. That’s where we get the ‘single digit’ – there actually is a second digit, only it’s empty.
So the column AAA actually has index 702, or 26×27. Which index does the column AAAA have? 26×27². The system of adding powers of the base works, only we changed bases midway through.
You can see the lopsidedness in the index lookup table (I’m not displaying all characters for brevity). Sane number systems have square tables. Excel’s is 26×27 (shown are 4×5).



your argument could be enhanced with the inclusion of survey units.
12 inches to a foot
3 feet in a yard
22 yards in a chain
10 chains in a furlong
8 furlongs in a mile
3 miles in a league
What. I had to websearch this because it sounds too silly, but apparently it's true.
But, really, even if it used saner numbers (like 12:3:24:8:3), it still feels nothing like a "metric dozenal" would look like. It's missing the two things the metric system did right: