this post was submitted on 30 Oct 2024
392 points (97.6% liked)
Science Memes
11047 readers
3140 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
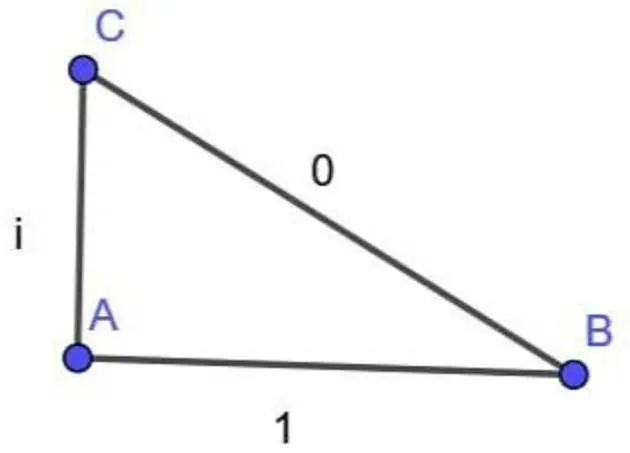
Isn't the squaring actually multiplication by the complex conjugate when working in the complex plane? i.e., √((1 - 0 i) (1 + 0 i) + (0 - i) (0 + i)) = √(1 + - i^2^) = √(1 + 1) = √2. I could be totally off base here and could be confusing with something else...
Almost:
Lengths are usually reals, and in this case the diagram suggests we can assume that A is the origin wlog (and the sides are badly drawn vectors without a direction)
Next we convert the vectors into lengths using the abs function (root of conjugate multiplication). This gives us lengths of 1 for both.
Finally, we can just use a Euclidean metric to get our other length √2.
Squaring isn't multiplication by complex conjugate, that's just mapping a vector to a scalar (the complex | x | function).
I think you're thinking of taking the absolute value squared, |z|^2 = z z*
Considering we're trying to find lengths, shouldn't we be doing absolute value squared?