this post was submitted on 25 Jul 2024
1145 points (99.2% liked)
Science Memes
10940 readers
1761 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
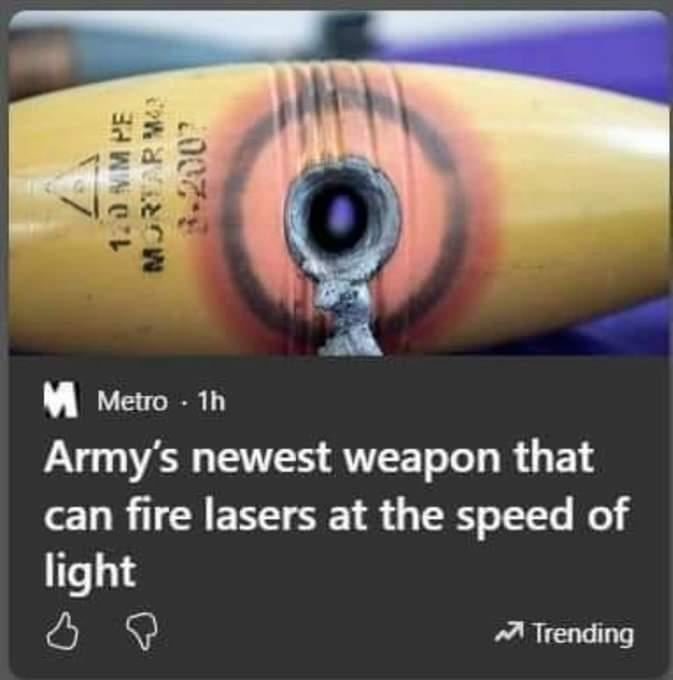
The medium that the laser goes through could slow it down, but it would still be insanely fast.
It would also still be the speed of light. Always is, unless you specify ‘in a vacuum’ every time.
The real fun starts when things move faster than the speed of light, that's when you get Cherenkov radiation!
Adding to the fun - The light is still going the same speed within the medium, but it's bumping into more things. Those collisions divert the light, lengthening the distance it travels through something like 1 cm of glass vs 1 cm in a vacuum. It changes the time it takes to travel through glass rather than the speed at which the light is moving.
At least that's what I remember from a YouTube video.
Probably the Youtube video in question
Yes that's it! Thanks for the link!!